Introduction
Your credit score is one of the most crucial numbers in your financial life. It determines your ability to get a loan, the interest rates you pay, and even your ability to rent an apartment or secure a job. Despite its importance, many people don’t fully understand how credit scores work, what affects them, and how to improve them. This blog will break down everything you need to know about credit scores and how they impact your finances.
What is a Credit Score?
A credit score is a numerical representation of your creditworthiness, typically ranging from 300 to 850. It is calculated based on your credit history and financial behavior. Lenders, landlords, and even some employers use your credit score to assess how responsible you are with money.
The most common credit scoring models in the U.S. are:
- FICO Score – Used by 90% of top lenders
- VantageScore – Another popular scoring model developed by major credit bureaus
Credit Score Ranges
| Credit Score Range | Rating |
|---|---|
| 300 – 579 | Poor |
| 580 – 669 | Fair |
| 670 – 739 | Good |
| 740 – 799 | Very Good |
| 800 – 850 | Excellent |
A higher credit score means better financial opportunities, while a lower score can make borrowing money difficult and expensive.
How is Your Credit Score Calculated?
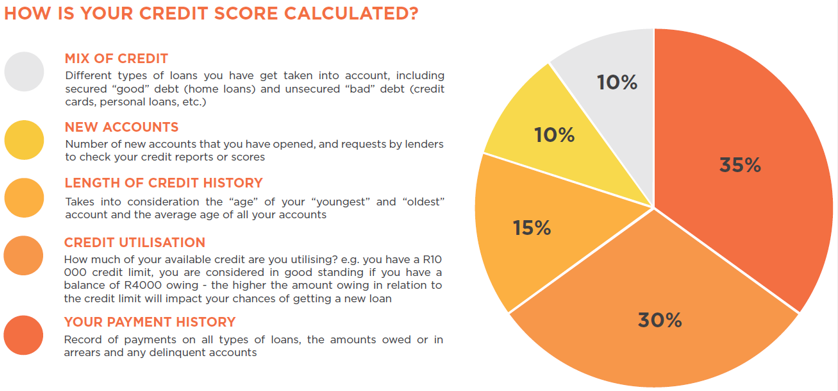
Credit scores are calculated using five main factors:
1. Payment History (35%)
This is the most crucial factor in your credit score. It reflects whether you’ve paid past credit accounts on time. Late payments, missed payments, or defaults can significantly damage your score.
2. Credit Utilization (30%)
This refers to how much of your available credit you’re using. Ideally, you should keep your credit utilization below 30% of your total credit limit.
For example, if you have a $10,000 credit limit and you’ve used $3,000, your credit utilization is 30%. Keeping it lower can help boost your score.

3. Length of Credit History (15%)
The longer your credit history, the better. This includes the age of your oldest account, your newest account, and the average age of all accounts.
4. Credit Mix (10%)
Lenders like to see that you can manage different types of credit, such as:
- Credit cards
- Auto loans
- Mortgages
- Personal loans
Having a mix of credit types can slightly improve your score.
5. New Credit Inquiries (10%)
Every time you apply for a new credit card or loan, a hard inquiry is added to your credit report. Too many inquiries within a short period can lower your score.
How Does Your Credit Score Impact Your Finances?
1. Interest Rates on Loans and Credit Cards
Your credit score directly affects the interest rates you get on loans and credit cards. A higher score means lower interest rates, saving you thousands over time.
For example:
- A person with an 800+ score might get a 3% mortgage rate
- A person with a 600 score might get a 6% mortgage rate
On a $300,000 home loan, that difference could mean paying $100,000 more in interest over 30 years!
2. Approval for Loans and Credit Cards
A low credit score can lead to loan denials or require you to get a co-signer. Even if you are approved, the terms might not be favorable.
3. Renting an Apartment
Landlords often check credit scores before renting out properties. A poor score could lead to higher security deposits or outright denial.
4. Employment Opportunities
Some employers check credit scores when hiring, especially for financial jobs. A bad credit score could cost you career opportunities.
5. Insurance Premiums
Many insurance companies use credit scores to determine rates. A low score can mean higher premiums for auto and home insurance.
How to Improve Your Credit Score
1. Pay Your Bills on Time
Since payment history is the biggest factor, always make at least the minimum payments on time. Setting up autopay can help.
2. Reduce Your Credit Utilization
Keep your credit usage below 30% and ideally under 10% for the best impact on your score.
3. Don’t Close Old Credit Accounts
Even if you don’t use a card, keeping it open helps maintain a long credit history.
4. Diversify Your Credit Mix
If possible, having a mix of credit types can improve your score. But don’t take on debt just to improve your mix.
5. Limit Hard Inquiries
Only apply for credit when necessary. Too many applications in a short period can harm your score.
6. Dispute Errors on Your Credit Report
Check your credit report regularly for mistakes and dispute them if necessary. You can get free credit reports from AnnualCreditReport.com.
Conclusion
Your credit score is a powerful financial tool that affects almost every aspect of your financial life. By understanding how it’s calculated and taking steps to improve it, you can secure lower interest rates, get better financial opportunities, and save money in the long run.
Start managing your credit wisely today, and set yourself up for a brighter financial future!