The Federal Reserve, often referred to as “the Fed,” plays a critical role in shaping the US economy, influencing interest rates, inflation, and employment levels. Its policies and actions have profound effects on the stock market, impacting investors, businesses, and consumers alike. Understanding how the Fed operates and its influence on financial markets can help investors make informed decisions and navigate market fluctuations.
Understanding the Federal Reserve
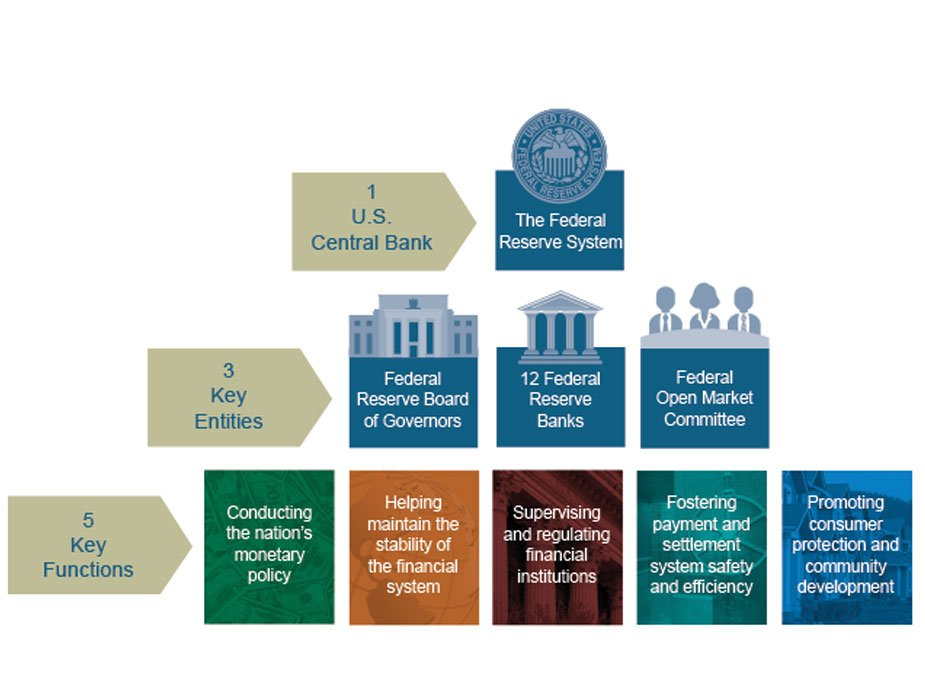
The Federal Reserve was established in 1913 to provide the United States with a stable and flexible financial system. It is the central banking system of the country, consisting of twelve regional banks, a Board of Governors, and the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC). The Fed’s primary mandate is to promote maximum employment, stabilize prices, and moderate long-term interest rates.
To achieve these objectives, the Federal Reserve employs various monetary policy tools, including setting interest rates, conducting open market operations, and adjusting reserve requirements for banks. These measures directly and indirectly influence the stock market by affecting investor sentiment, corporate profitability, and overall economic activity.
How the Federal Reserve Affects the Stock Market
The Federal Reserve’s monetary policies can significantly impact the stock market in several ways:
- Interest Rates and Stock Valuations: One of the most influential tools the Fed has is the federal funds rate, which is the interest rate at which banks lend to one another overnight. When the Fed lowers interest rates, borrowing becomes cheaper, encouraging businesses to expand and consumers to spend more. This can lead to higher corporate earnings, boosting stock prices. Conversely, higher interest rates can make borrowing more expensive, slowing economic growth and potentially leading to a stock market downturn.
- Inflation Control and Market Stability: The Fed monitors inflation closely, using monetary policies to keep it within a target range. If inflation rises too quickly, the Fed may increase interest rates to cool down the economy. While this can stabilize prices, it often leads to market volatility as investors adjust their expectations for future earnings and economic growth.
- Quantitative Easing and Market Liquidity: During economic downturns, the Fed may engage in quantitative easing (QE), purchasing government securities and other assets to inject liquidity into the financial system. QE can drive stock prices higher by lowering yields on bonds, making equities more attractive to investors.
- Market Sentiment and Investor Behavior: The Fed’s statements, meeting minutes, and press conferences can significantly influence investor sentiment. Even hints of potential rate hikes or changes in monetary policy can trigger market fluctuations, as traders and institutions react to anticipated shifts in economic conditions.
Historical Examples of the Fed’s Influence on the Stock Market
- 2008 Financial Crisis: In response to the Great Recession, the Fed slashed interest rates to near-zero levels and launched aggressive quantitative easing programs. These measures helped stabilize the stock market and fuel one of the longest bull markets in history.
- COVID-19 Pandemic Response: In 2020, the Fed took swift action by cutting interest rates, introducing massive stimulus programs, and purchasing bonds to support the economy. The stock market initially crashed but rebounded rapidly, driven by the Fed’s interventions.
- Recent Interest Rate Hikes: In 2022 and 2023, the Fed raised interest rates to combat rising inflation. This led to increased market volatility, as investors reassessed stock valuations and economic growth projections.
How Investors Can Navigate Fed-Driven Market Changes
Given the Fed’s influence, investors should consider the following strategies to manage their portfolios effectively:
- Diversification: Holding a mix of asset classes, including stocks, bonds, and commodities, can help mitigate risk during periods of monetary policy shifts.
- Monitoring Economic Indicators: Keeping an eye on inflation, employment data, and Fed announcements can provide insights into potential market movements.
- Long-Term Perspective: While short-term volatility is common, focusing on long-term investment goals can help weather fluctuations caused by Fed policies.
- Sector Rotation: Certain sectors, such as financials and utilities, may perform differently depending on interest rate changes. Adjusting portfolio allocations accordingly can enhance returns.
Conclusion
The Federal Reserve plays a pivotal role in shaping the US stock market through its monetary policies, interest rate decisions, and economic interventions. Understanding how the Fed’s actions impact the market can help investors make informed decisions and develop strategies to navigate economic cycles effectively. By staying informed and adapting to policy changes, investors can position themselves for long-term financial success.