Stock market volatility is an essential aspect of financial markets, often viewed with both concern and opportunity by investors. While some see it as a sign of risk and uncertainty, others recognize it as a chance to capitalize on market movements. Understanding the causes and effects of stock market volatility can help investors make informed decisions and navigate unpredictable economic landscapes.
What Is Stock Market Volatility?
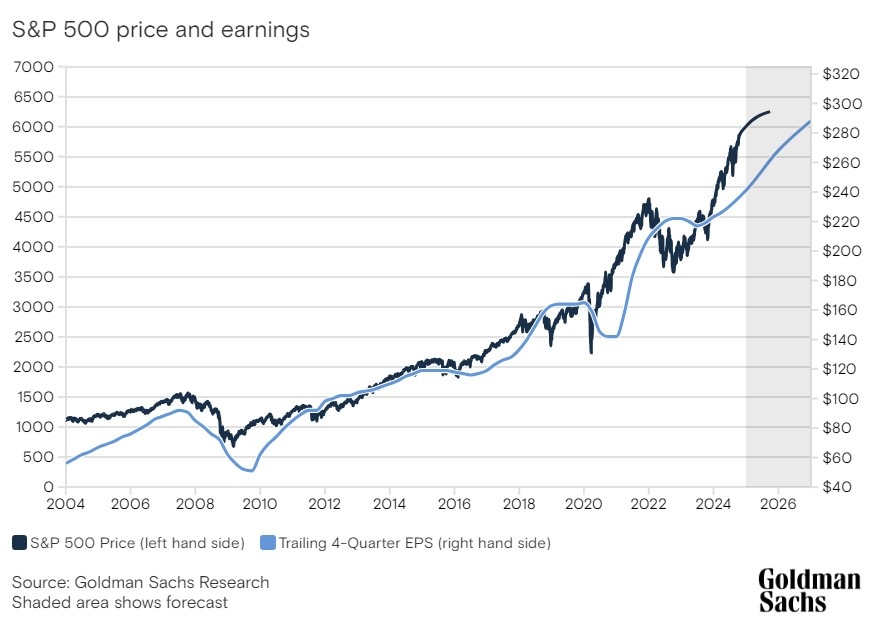
Stock market volatility refers to the degree of variation in stock prices over time. It is typically measured by statistical indicators such as the standard deviation or the volatility index (VIX), often referred to as the “fear index.” High volatility indicates significant price swings within a short period, while low volatility suggests a more stable market.
Causes of Stock Market Volatility
Economic Data and Indicators
One of the primary drivers of stock market volatility is economic data. Reports on GDP growth, employment rates, inflation, and consumer spending can influence investor sentiment. Positive economic data can drive stock prices higher, while negative data can create uncertainty and cause sell-offs.
Interest Rate Changes
Interest rates set by the Federal Reserve play a significant role in stock market movements. When interest rates rise, borrowing costs increase, which can reduce corporate profits and discourage investment. Conversely, lower interest rates make borrowing cheaper, often boosting stock prices.
Corporate Earnings Reports
Quarterly earnings reports provide insights into a company’s financial health. Strong earnings can lead to stock price surges, while disappointing results can trigger sell-offs. Investors closely monitor earnings guidance to anticipate future performance.
Political and Geopolitical Events
Political instability, trade wars, and geopolitical tensions can cause uncertainty in the stock market. Elections, policy changes, and international conflicts can lead to unpredictable market movements, as investors assess the potential impact on economic stability.

Market Speculation and Investor Sentiment
Investor psychology plays a crucial role in stock market volatility. Speculative trading, herd behavior, and media influence can amplify market movements. Fear and greed often drive short-term fluctuations, leading to rapid price changes.
Supply Chain Disruptions and Global Events
Events such as pandemics, natural disasters, and supply chain disruptions can significantly impact the stock market. The COVID-19 pandemic, for example, led to extreme volatility as businesses faced unprecedented challenges and uncertainties.
Effects of Stock Market Volatility
Impact on Investors
Stock market volatility can be a double-edged sword for investors. While it creates opportunities for short-term gains, it also increases the risk of significant losses. Long-term investors may experience temporary declines in portfolio value but can benefit from market recoveries over time.
Influence on Consumer Confidence
Fluctuating stock prices can affect consumer confidence and spending behavior. A declining market can create fear and uncertainty, leading consumers to cut back on spending, which can slow economic growth.
Corporate Decision-Making
Businesses rely on stable financial markets for expansion, investment, and fundraising. High volatility can discourage companies from launching IPOs, issuing new stock, or making large-scale investments, potentially slowing economic progress.
Effect on Retirement Funds
Many retirement funds, such as 401(k) plans, are tied to stock market performance. Market downturns can erode retirement savings, causing concerns for retirees and those nearing retirement.
Trading Opportunities
For active traders, volatility presents opportunities for profit. Short-term traders and hedge funds often thrive in volatile conditions by capitalizing on rapid price movements. Strategies such as options trading and short selling become more prevalent in uncertain markets.
Strategies to Manage Stock Market Volatility
Diversification
Spreading investments across various asset classes can help mitigate the impact of volatility. A well-diversified portfolio reduces exposure to any single stock or sector.
Long-Term Investing
Staying invested for the long term allows investors to ride out market fluctuations. Historically, the stock market has shown resilience and growth over extended periods.
Risk Management
Utilizing stop-loss orders, setting realistic investment goals, and understanding risk tolerance can help investors navigate volatile markets effectively.
Monitoring Market Trends
Keeping an eye on economic indicators, corporate earnings, and global events can help investors make informed decisions and adjust their portfolios accordingly.
Conclusion
Stock market volatility is a natural part of investing, driven by various economic, political, and psychological factors. While it can create uncertainty, it also presents opportunities for strategic investors. Understanding the causes and effects of market fluctuations can help investors develop sound investment strategies, minimize risks, and capitalize on market movements. By maintaining a long-term perspective and implementing risk management techniques, investors can successfully navigate volatile markets and achieve their financial goals.