Investing in the stock market can be a profitable endeavor if approached with the right analysis techniques. Professional investors use a combination of fundamental analysis, technical analysis, and sentiment analysis to make informed decisions. This guide will walk you through the key steps and methodologies used by seasoned investors to evaluate stocks effectively.
Understanding Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental analysis focuses on evaluating a company’s financial health, competitive advantage, and overall market position. This involves examining financial statements, assessing industry trends, and considering macroeconomic factors.
- Financial Statements: Investors review a company’s income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement to gauge profitability, liquidity, and financial stability.
- Earnings Per Share (EPS): A key metric that indicates a company’s profitability. Higher EPS usually signals a stronger financial position.
- Price-to-Earnings (P/E) Ratio: Compares a company’s stock price to its earnings. A lower P/E might indicate an undervalued stock, while a high P/E could suggest overvaluation.
- Debt-to-Equity Ratio: Helps assess the company’s financial leverage. A lower ratio suggests lower financial risk.
- Return on Equity (ROE): Measures profitability in relation to shareholders’ equity. A higher ROE is often preferred.
Additionally, understanding a company’s competitive advantage, market share, and management team plays a crucial role in fundamental analysis.
Technical Analysis for Stock Evaluation
Technical analysis involves studying stock price movements and trading volumes to predict future price trends. This method relies on historical price data and market trends rather than financial statements.
- Moving Averages: Investors use simple moving averages (SMA) and exponential moving averages (EMA) to smooth out price fluctuations and identify trends.
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): A momentum indicator that signals whether a stock is overbought or oversold.
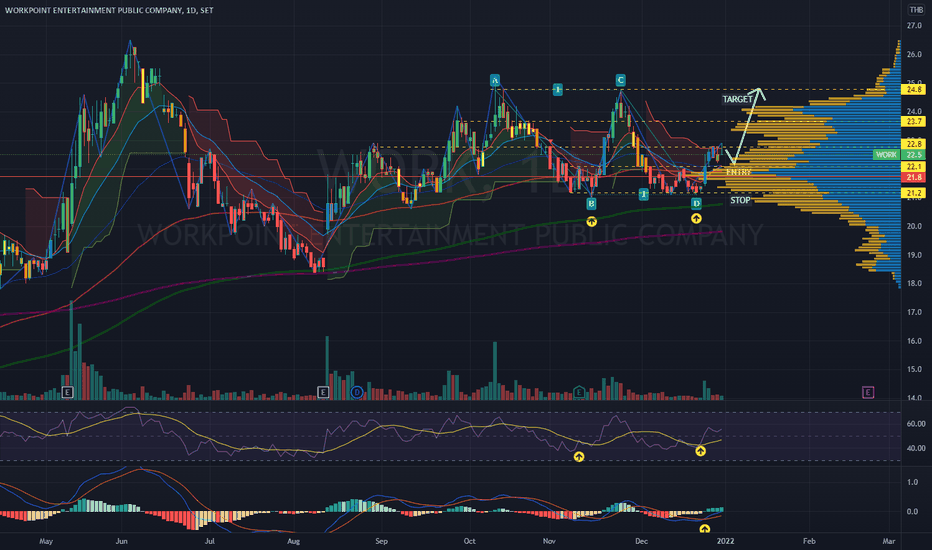
- Support and Resistance Levels: Price points where a stock historically stops declining or rising, helping investors determine entry and exit points.
- Candlestick Patterns: Certain formations, such as doji, hammer, and engulfing patterns, provide insights into market sentiment and potential trend reversals.
While technical analysis is often favored by short-term traders, long-term investors also use it to refine their entry and exit strategies.

Sentiment Analysis and Market Trends
Stock prices are also influenced by investor sentiment, news, and market trends. Professional investors analyze market sentiment using various sources, including:
- News and Earnings Reports: Major news events, earnings surprises, and regulatory changes can significantly impact stock prices.
- Social Media and Analyst Opinions: Twitter, Reddit, and financial news platforms can indicate public sentiment and potential trends.
- Institutional Investor Activity: Watching the investment patterns of hedge funds and institutional investors can provide valuable insights into market movements.
Key Metrics and Ratios Used by Professionals
To analyze stocks effectively, professional investors rely on specific financial metrics and ratios:
- PEG Ratio (Price/Earnings to Growth): Accounts for future earnings growth, offering a more comprehensive valuation.
- Dividend Yield: Measures how much a company pays out in dividends relative to its stock price.
- Free Cash Flow (FCF): The cash remaining after a company covers its operational and capital expenditures, indicating financial health.
- Market Capitalization: Helps investors understand the company’s size and risk profile.
- Beta Coefficient: Measures stock volatility relative to the overall market, helping investors assess risk.
Developing a Stock Analysis Strategy
Professional investors follow a structured approach when analyzing stocks:
- Define Investment Goals: Determine whether the investment is for long-term growth, dividend income, or short-term trading.
- Conduct Sector and Industry Analysis: Compare the stock’s performance to industry peers and market trends.
- Use a Combination of Analysis Techniques: A blend of fundamental, technical, and sentiment analysis provides a comprehensive evaluation.
- Diversify the Portfolio: Investing in a mix of stocks across different industries helps reduce risk.
- Stay Updated with Market News: Regularly review financial reports, economic indicators, and market conditions.
Conclusion
Analyzing stocks like a professional investor requires a combination of financial knowledge, research skills, and market awareness. By mastering fundamental analysis, technical indicators, and sentiment analysis, investors can make informed decisions and enhance their portfolio performance. With a disciplined approach and continuous learning, anyone can develop the skills needed to navigate the stock market effectively.